Development and validation of RP-HPLC method for estimation of Cefotaxime sodium in marketed formulations
- *Corresponding Author:
- Lalitha N
Department of Quality Assurance, Al-Ameen College of Pharmacy, Bangalore, India.
E-mail: lallubalu@rediffmail.com
Date of Received: 30-01-2010
Date of Modified: 02-02-2010
Date of Accepted: 05-01-2010
Available Online: 15-02-2010
Abstract
A rP-HPLC assay method has been developed and validated for cefo- taxime. An isocratic rP-HPLC was developed on a ss Wakosil II- C8 column (250 mm 4.6 mm i.d., 5 µm) utilizing a mobile phase of ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.8) and acetonitrile (85:15 v/v) with UV detection at wavelength 252 nm at the flow rate 0 .8 ml/min. the proposed method was validated for sensitivity, selectivity, linearity, accu- racy, precision, ruggedness, robustness and solution stability. the response of the drug was linear in the concentration range of 10-70 µg/ml. Limit of detection and Limit of quantification was found to be 0.3 µg/ml and 0.6 µg/ml respectively. the % recovery ranged within 97-102 %. Method, system, interday and intraday precision was found to be within the limits of acceptance criteria. Method was found to be rugged when analysis was carried out by different analyst. the method was found to be sensitive and efficient with 2216 theoretical plates, 0.1128 mm HEtP and tailing factor 1. the method was suitable for the quality control of cefotaxime in injection formulations.
Keywords
HPLC Methanol Acetonitrile Cefotaxime sodium Validation
Introduction
Cefotaxime sodium is sodium 7-[2- (2-amino-4-thiazolyl) glyoxylamido]-3- (hydroxymethyl)-8-oxo-5-thia-1-azabicyclo [4.2.0] oct-2-ene-2-carboxylate 72 (Z)-(o-methyloxime), acetate (ester). (Fig 1) with molecular formula C16H16N5NaO7S2. [1] It is a 1st generation cephalosporin, inhibits cell wall biosynthesis. Literature survey revealed that ESR [2], various spectrophotometric and HPLC methods are available for estimation of cefotaxime sodium.[3-17] In the present study a simple rapid precise and accurate RP-HPLC method was developed for the estimation of cefotaxime sodium.
| Sl. No. | Std. cefotaxime conc. mcg/ml (a) | Sample cefo- taxime conc. mcg/ml (b) | Total conc. mcg/ml (c) | Peak area | Total amount of cefotaxime from Std graph mcg/ml (d) | Recovery of standard drug mcg/ml (d-b) = (e) | % Recovery of standard (e x 100 / c) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 10 | 10 | 20 | 979221 | 19.70 | 9.70 | 97.05 |
| 2 | 30 | 10 | 40 | 2006242 | 41.63 | 31.63 | 101.23 |
| 3 | 50 | 10 | 60 | 3034843 | 61.06 | 51.06 | 102.12 |
Table 1: Recovery study data of cefotaxime.
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Calibration ranges (mcg/ml) | 10–70 |
| Slope | 49692 |
| Intercept | 87045 |
| Correlation coefficient (R2 ) | 0.9976 |
| Regression | 49692x+87045 |
Table 2: Regression Analysis of the Calib ration Curves for Proposed Method
| Parameters | Values |
|---|---|
| Detection limit (mcg/ml) | 0.3 |
| Quantitation limit (mcg/ml) | 0.6 |
| Accuracy (%) | 97 to 102% |
| Precision (RSDa) | |
| Intraday (n = 3) | 1.2917 |
| Interday (n = 3) | 0.9050 |
| Repeatability (RSDa , n = 3) | 0.1659 |
| Ruggedness (% Assay) | |
| Analyst 1 | 99.51 |
| Analyst 2 | 99.34 |
Table 3: Summary of validation parameters
Materials and Methods
Pure Cefotaxime was obtained as gift sample from Karnataka Antibiotics Pharmaceuticals Ltd, Bangalore, India. Cefotaxime Injection was purchased from local market. HPLC grade methanol was purchased from Qualigens fine chemicals, Mumbai, India. Millipore water was obtained from the Millipak 0.22μm filter. Buffer materials and all other chemicals were of analytical-reagent grade. An HPLC system consisted model 10AT Shimadzu- SPD10A detector, the column used was a SS Wakosil II- C8 (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm). The separation was carried out under isocratic elution of the mobile phase, ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.8) and acetonitrile in the ratio of (85:15 v/v) at the flow rate 0 .8 ml/min. The column temperature was ambient, the wavelength was monitored at 252 nm and the injection volume was 100 μl. Standard stock solution of 1 mg/ml of cefotaxime in mobile phase was prepared in 10 ml volumetric flask. Working solutions were prepared by diluting the aliquots of stock solutions with the mobile phase to contain 0.1–100 μg/ml of standard cefotaxime. 100 μl of each working standard solution was injected into the chromatograph and chromatogram was recorded. The standard calibration curve was constructed in the concentration range of 5-100 μg/ml, with concentration on X- axis, peak area on Y- axis and regression equation was calculated.
Accurately weighed 10 mg of cefotaxime sodium injection dissolved in 10 ml mobile phase, from this solution working sample solution of 10 μg/ml was prepared with the mobile phase in 10 ml volumetric flask and filtered through a 0.22 μm nylon syringe filter. 100μl of working sample solution was injected into the chromatograph and chromatograph was recorded. The concentration of cefotaxime in working sample solution was calculated from regression equation using average peak area of three replicates of working sample solution. The developed analytical method was validated as per ICH method validation guidelines. The validation parameters addressed were LOD, LOQ, linearity, accuracy, precision (system, method, inter-day and intra-day), robustness, ruggedness, specificity and stability of cefotaxime in mobile phase.
Results and Discussion
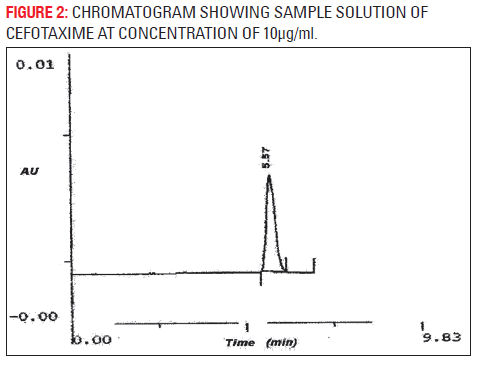
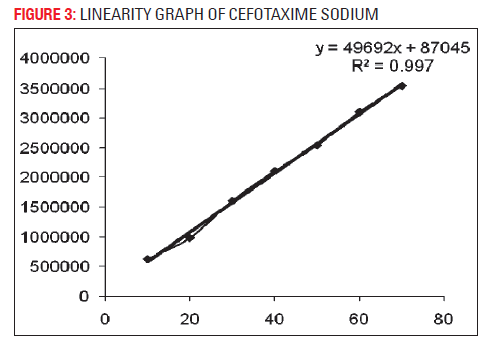
The developed analytical method was validated as per ICH method validation guidelines (Table 1). The validation parameters addressed were LOD, LOQ, linearity, accuracy, precision (system, method, inter-day and intra-day), robustness, ruggedness, specificity and stability of cefotaxime in mobile phase. A simple and rapid isocratic RP-HPLC method for estimation of cefotaxime was developed on a SS Wakosil II- C8 column (250 mm × 4.6 mm i.d., 5 μm) utilizing a mobile phase of ammonium acetate buffer (pH 6.8) and acetonitrile (85:15v/v) with UV detection at wavelength 252 nm at the flow rate 0.8 ml/min. Cefotaxime was eluted at retention time 5.47 min (Fig. 1). Three independent determinations were performed at each concentration and the response for the drug was found linear in the concentration range of 10 to 70 μg/ml. The standard calibration curve was plotted and regression equation was calculated as y = 49692x+87045 with R2 = 0.9976 (Fig. 2), percentage recovery ranges from 97–102% (Table 1). The method was found to be specific for the estimation of cefotaxime in marketed injection formulations. The method was found to be sensitive and efficient with 2216 theoretical plates, 0.1128 mm HETP and tailing factor 1. The developed method was successfully applied for the assay of marketed formulation, the working sample solution showed 97.33 % w/w of cefotaxime sodium.
Conclusion
The study presents a reverse phase HPLC estimation of cefotaxime with UV-detector. Method is simple, economical and less time consuming that the other prescribed methods. The method was validated and found specific, accurate, precise, rugged and robust. The method could be applied with success even to the analysis of marketed products cefotaxime injection formulation, as no interference was observed due to excipient or other components present.
Acknowledgements
Highly thankful for Karnataka Antibiotics and Pharmaceuticals Ltd Bangalore, for providing the gift samples, and to all my research colleagues for their support in the work.
References
- USP-27-NF, The United States Phamacopoeial Convection Inc. Rockville, MD; 2004:328-330.
- Basly JP, Basly I and Bernard M. ESR spectroscopy applied to the study of the pharmaceuticals radiosterilization:cefoperazone. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 1998 Aug; 17(4-5):817- 875.
- Reddy MN, Reddy VPN, Reddy PJC et.al Spectrophotometric Determination of Cefuroxime Sodium in Pharmaceutical Dosage Forms. The Antiseptics 2002; 99(3): 88-89.
- Nkeoma NO, Godwin IC. Nwokedi et.al. Spectrophotometric determination of some cephalosporin antibiotics using Prussian blue reaction. Sci. Res. Essay 2007 Aug; 2 (8): 342- 347.
- SA Patel, NM Patel, MM Patel. Spectrophotometric estimation of cefotaxime and ceftriaxone in pharmaceutical dosage forms 2006; 68(1): 101-103.
- Nabi SA, Laig E, Islam A. Selective separation and of Determination Cephalosporins by TLC on Stannic oxide layers. Acta Chromatographica. 2004;14: 92-101.
- Zendelovska, Traj stafilov, Petar miloševski. Bull. Chem. Technol. Macedonia High-performance liquid chromatographic method For determination of cefixime and cefotaxime in human plasma. Dragica, 2003; 22(1): 39–45
- Nabi SA, Laig E, Islam A. Selective separation and of Determination Cephalosporins by TLC on Stannic oxide layers. Acta Chromatographica. 2004; 14: 92-101.
- Dragica zendelovska, Traj e stafilov and Petar miloševski. High-performance liquid chromatographic method For determination of cefixime and cefotaxime in human plasma Bull. Chem. Technol. Macedonia, 2003; 22(1): 39–45.
- Snyder L R, kirkand J, gloch JL. Practical HPLC Method Developed. 5th ed. a wiley inter sedent publication; 2002: 402-420.
- Papadoyannis D, Ioannis N and Victoria F. HPLC determination of cefotaxime and cephalexine residues in milk and cephalexine in veterinary formulation Samanidou, Microchimica Acta.2008 April; 160(4): 471-475.
- Rosseel M.T and Vandewoude K.H. Liquid chromatographic determination of the plasma concentrations of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime in plasma of critically ill patients J. Chromatography B 2004 Nov; 811( 2);25:159-63.
- Mara M. Aleksi? Vera Kapetanovi?, Jasmina Atanackovi?, et al Simultaneous determination of cefotaxime and desacetylcefotaxime in real urine sample using voltammetric and high-performance liquid chromatographic methods.Talanta. 2008 Oct ;77(1):131-137.
- Signs SA, File TM and Tan JS. High-pressure Liquid Chromatographic Method for Analysis of Cephalosporins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1984; 26:652-655.
- Joshi S. HPLC separation of antibiotics present in formulated and unformulated samples. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal 2002; 28:795-809.
- Steven AS, Thomas MF and James ST. High Pressure Liquid Chromatographic Method for Analysis of Cephalosporins. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother 1984; 26:652-655.
- www.statisticaloutsourcingservices.com/ methval.