Antioxidant and protective effect of “Artemesia absinthium” and “Nigella sativa ” on Albino mice mode of hepatic injury
2 Department of Bioinformatics and Biotechnology, Government College University, Faisalabad, Pakistan
3 Department of Pharmaceutical Toxicology, Hacettepe University, Ankara, Turkey
4 Hacettepe University Vaccine Institute, Vaccine Technologies USA, Ankara, Turkey
5 Department of Pharmacy, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, China
6 Department of Pharmacy, Wageningen University & Research, Netherlands
7 Department of Biotechnology, University of Health Sciences, Lahore, Pakistan
Received: 01-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. Jbclinphar-22-59213; Editor assigned: 04-Mar-2022, Pre QC No. Jbclinphar-22-59213; Accepted Date: Mar 28, 2022 ; Reviewed: 18-Mar-2022 QC No. Jbclinphar-22-59213; Revised: 24-Mar-2022, Manuscript No. Jbclinphar-22-59213; Published: 31-Mar-2022, DOI: 10.37532/0976- 0113.13(2).136
Citation: Mazhar MW. Antioxidant and protective effect of “Artemesia absinthium” and “Nigella sativa ” on Albino mice mode of hepatic injury. J Basic Clin Pharma 2021;13(2):136-139.
This open-access article is distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (CC BY-NC) (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/4.0/), which permits reuse, distribution and reproduction of the article, provided that the original work is properly cited and the reuse is restricted to noncommercial purposes. For commercial reuse, contact reprints@jbclinpharm.org
Abstract
Background: Ethanoic plant extract of N.sativa and A.absinthium has compounds that act as anti-inflammatory, cardio protective, anticancer, and antioxidant. The flavonoids and reducing power in these plants are used to treat liver injury. In this research, we explored the protective effect of these plants on APAP-induced liver injury. Methodology: Albino mice were treated with extract of both plants separately and then used in combined form for 14 days, the results show the protection against injury induced in the 23 liver by APAP (220 mg/kg). In vitro study, the plants extract shows phytochemical compounds by pre-treatment assay, reducing assay, and DPPH assay. In this study, albinos were categorized into 5 groups, group I was the control group that received only distilled water, and group II received 220 mg/kg Acetaminophen by intraperitoneal injection. Group III received 350 mg/kg ethanolic extract of N.sativa and received 220 mg/kg acetaminophen. Group IV received 350 mg/kg ethanolic extract of Artemisia absinthium and received 220 mg/kg acetaminophen. Group V received both 500 mg/kg ethanolic extract of N.sativa and A.absinthium and received 220 mg/kg acetaminophen. Results: The results indicate that the extract of N.sativa and A.absinthium decreased the AST and ALT level in serum in exposed APAP mice. However, the combined form of both extracts decreased the LFTs in blood serum. Conclusion: This study proved that the plant extract is used against APAP hepatic injury and it is also associated with oxidative stress in the body. And the combined extract maybe use as a therapeutic agent against hepatitis.
Keywords
Antioxidant activity, TPC, TFC, DPPH, Artemesia absinthium, Nigella sativa, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Antibacterial, Anticancer activity.
Introduction
Acute hepatitis and hepatocellular carcinoma are severe medical conditions due to the release of inflammatory cytokines. (IL-6, TNF-α, and INF-γ), elevated ALT /AST, cell regulation stop that progress to fibrosis cirrhosis and cancer [1]. Viruses like HCV and HBV, toxins, autoimmune alcohol, metabolic disorders like Williamsons, obesity, diabetes, drugs are the main risk factor of liver pathogenicity [2]. Xenobiotics compound absorbed into the gut and then transported to the liver for metabolism. During metabolisation, some toxic intermediates generated and damage the liver parenchymal cells and hepatocyte cells [3].
Due to mortality, Hepatocellular carcinoma ranks second among all cancers. Pakistan has the highest prevalence rate of hepatitis C and it's known as a risk factor of HCC [4]. HCC is treated with immune suppressive therapies which are associated with sides effects like osteoporosis and hyperglycaemia [5].
The liver involves in different functions like metabolic, detoxifications, chemical transformation, excretory, and supporting other organs [6]. Traditional medicines use as protection against cancer. Green tea extracts have a hepato protective compound that uses against APAP to induce hepatotoxicity [7]. Ficus carica is commonly known as anjeer, used for medical purposes in India. Another plant Bauhinia purpurea L., commonly known as kachnar, is used to treat stomach ulcers, ulcer wounds, fever, diarrhoea, and swelling [8].
Methodology
Chemicals
Chemicals were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich except for Folin-Cioacalteu’s. Disodium phosphate buffer solution purchased from Fisher Scientific.
Collection of plant sample
N.sativa was collected from the market that was available in herbal shops. Fully maturated A. absinthium plant with their roots collected from northern areas of Pakistan. Collected specimens were dried at room temperature and stored for further use.
Preparation of plant extracts
The leaves and seeds of A.absinthium and N.sativa were washed carefully with distilled water and crushed into fine powder. 100 g of powder sample soaked in ethanol for 48 h at room temperature. The solid particles were removed from the solvent with the help of fine cloth and concentrated solvent at 50-600°C by using a rotatory evaporator. The extract was stored at -20°C for further use.
In vitro studies
Total phenolic assay: 70 mg of the dry mass of plant extract was mixed with 0.7 ml of Folin-ciocalteu reagent and 7.5 deionized water. Check absorbance at 755 nm at spectrophotometer. Results were expressed as mg/ml gallic acid equivalents.
Total flavonoids assay: Total flavonoids detection by Chin and Li method. The solution absorbance was measured at 510 nm in a spectrophotometer. The results were expressed as catechin equivalents per dry mass.
DPPH assay
2-2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl radical-scavenging activity was determined by Brand-Williamson’s method. The absorbance was measured at 750 nm, all determinations were analysed in a triplicate manner.
Experimental animals
The male Swiss albino mice were used for this study and their weight was 28-32 g. Animals were housed in cages and maintained temp at 25 ± 2°C with light and dark cycle 12/12. These were provided with better nutrition.
Experimental protocols
All the animals were categorized into 5 groups, group I was the control group that received only distilled water for 14 days and group II receiving 220 mg/kg acetaminophen by intraperitoneal injection. Group III received 350 mg/kg ethanolic extract of N.sativa for 14 days and received 220/mg acetaminophen and group IV received 350 mg/kg ethanolic extract of Artemisia Absinthium for 14 days and received 220/mg acetaminophen. Group V received both 500 mg/kg ethanolic extract of N. Sativa and A. absinthium for 14 days and received 220/mg acetaminophen. On the 15th day, all animals received acetaminophen via IP injection with the respective dose mentioned above except the control group.
All animals were anesthetized with light chloroform and sacrificed by cervical decapitation on the 15th day after the final dose. The blood samples were collected in gel vials for serum preparation. Hepatotoxicity was indicated by a significant elevation in ALT and AST in acetaminophen mice as compared to controls.
Biochemical investigation
After collection of blood, serum was separated by using a centrifugation machine at 4000 rpm for 15 minutes. ALT, AST, Total bilirubin, and alkaline phosphatase enzyme were evaluated by adopting kit procedures at the LTM-9200 chemistry analyser [9].
Statistical analysis
The statistical analysis was performed by Graph Pad Prism software 9.3.1.471. The data were represented as mean ± SD and the data were subjected to one-way ANOVA
Results
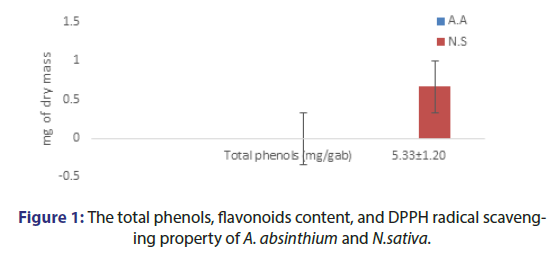
A.absinthium exhibits the total phenolic compound 5.79 ± 1.20 mg gallic acid equivalent /g of dry plant extract and total flavonoid content 132.55 ± 2.29 mg catechin equivalent. N.sativa exhibits the total phenolic compound 7.46 ± 2.49 mg gallic acid equivalent/g of dry plant extract and total flavonoid content 47.89 ± 5.14 mg catechin equivalent. The A. absinthium and N.sativa have DPPH radical scavenging property and 25 ug/ml exhibit 35.17 ± 1.19 and 24.69 ± 2.17 respectively (Table 1 and Figure 1)
| Content | % Yield | Total phenols (mg/gab) | Total flavonoids (mg/gac) | Total flavonoids mg/g of extract | Total phenolic mg/g of extract | DPPH radical scavenging at 25 ug/ml extract |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| A. Absinthium | 13.02% | 5.33 ± 1.20 | 135.55 ± 2.29 | 0.67 | 0.1 | 35.17 ± 1.19 |
| N.sativa | 10.66% | 7.46 ± 2.49 | 49.15 ± 4.83 | 0.16 | 0.12 | 24.69 ± 2.17 |
Note: ab Phenols; ac Flavonoids
Table 1: The total phenols, flavonoids content, and DPPH radical scavenging property of A. absinthium and N.sativa.
The reducing power of tested samples is directly proportional to sample concentration. The reducing power at 200 ug/ml was 0.468 for A. absinthium and 0.637 for N.sativa.
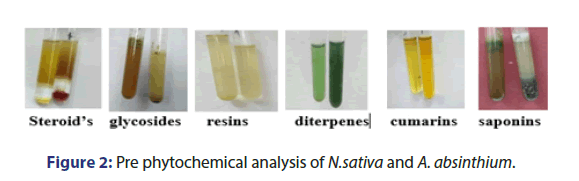
Pre phytochemical analysis
In this study, dried extraction was obtained from both species. Pre-Phytochemical analysis shows the presence of saponins, glycosides, diterpenes, glycosides, and steroids in N.sativa and A. absinthium in Figure 2.
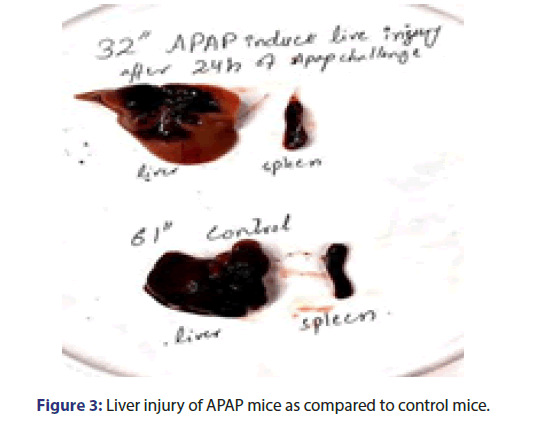
Liver Injury
500 mg/kg dose of APAP given to mice and compare with control group mice. As shown in the picture the challenged Albino mice's large liver lobe colour changed into a pick, the phenotypically changes in the liver that tells us about the liver injury (Figure 3).
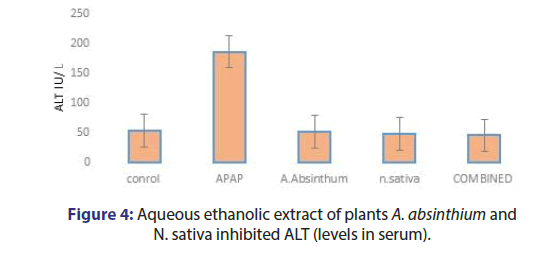
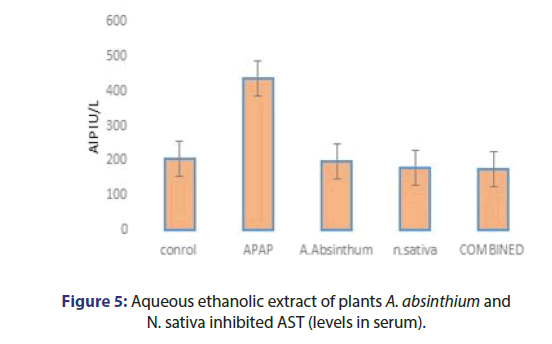
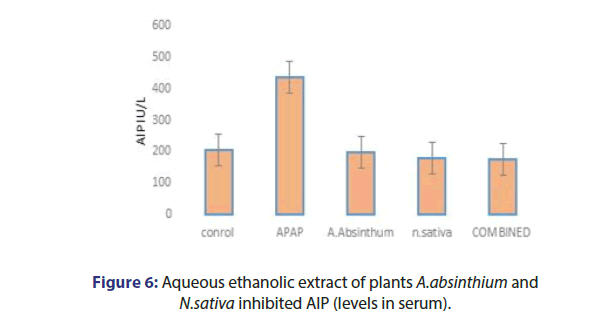
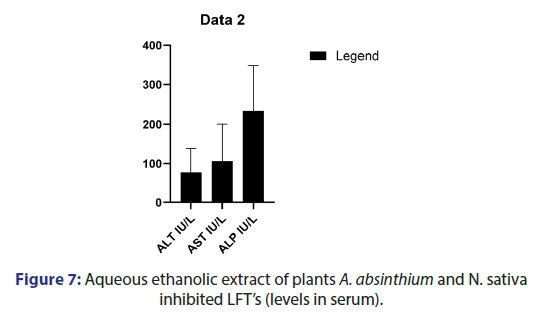
The effect of plant extracts, acetaminophen caused liver damage in mice as evidenced by changes in hepatic enzymes LFTS. The normal ALT value 54 IU/L increases 186 IU/L, AST value 144 IU/l was elevated to 256 IU/L, and ALP level 205 IU/L increases 436 IU/L by APAP intoxication. The A. absinthium and N.sativa 350 mg /kg the ALT mean value observed 51.78 IU/L and 48.27 IU/L Respectively. Combined plant extract group ALT and AST mean value observed as 45.79 IU/L and 44.1 IU/L. Bilirubin has no minor changes and the ALP mean value was observed as 178.5 IU/L (Figures 4-7).
Discussion
The process of the discovery of drugs is becoming more complex and more critical. Especially, the screening of the plants having anticancer activity has been increased since the few past decades. The approach for the screening and identification of the medicinal plan is based on ecological, ethno pharmacological, and chemo systemic information. Some of the institute research on hepatitis is working for the screening of the compounds having anticancer activity from the medicinal plants.
There exist many approaches for the researchers, but the more convenient method is the APAP which is usually used commonly in health labs to treat the liver injury in vivo. APAP model provides many opportunities for the researchers to investigate the mechanism of treatment of hepatitis disease. So, liver injury including cirrhosis even hepatocellular carcinoma can be treated by adopting the APAP approach.
There are many plants such as A. absinthium and N.sativa that have been reported, to have protective effects against acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity in mice. Another plant is known as ‘’Sal’’ which alleviates oxidative damage in the livers of albino mice. All these findings suggest that medicinal plants play important role in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma [10, 11].
The present study tells that the combined extract of both plants reduces the ALT, AST, and acts as an anti-inflammatory agent against PARP-induced liver injury. After IP Injection, PARP absorb in the liver and binds with glycoproteins that are mannose-rich glycoproteins and they present on sinusoidal endothelial cells of the liver and activates the CD+ T cells and then T cells secrete interleukins, cytokines, and adipokines. When infection occurs the elevation of transferases occurs in the blood. In this study, the results show that the extract of both plants suppressed the release of cytokines in the liver, and the inflammatory reaction inhibited by extract in APAP induced liver injury [12].
Plants have natural products that play role in human health and other illness because they have bioactive compounds. The phenolic, flavonoids, and carbohydrates are bioactive compounds and also affect cells [13]. In this study, both plants have these compounds that act as anti cancerous and protective properties.
ROS is the major product of the metabolic process; it causes oxidative stress in cells and leads to liver injury. Natural compounds have antioxidant properties and are used in the treatment of liver injury [14]. In this study, a DPPH assay was used to access the free radicals potentials in both plants. The antioxidant activity of natural products is performed by DPPH scavenging activity and power reduction.
PARP-induced liver injury is the common leading hepatic injury. Hepatocellular injury due to excessive level of PARP that increases the level of AST and ALT in blood. Generally, ALT and AST enzymes are used as biomarkers of liver disorders [15]. In our study significantly higher level of aminotransferases is due to higher PARP induction in liver injury. A. absinthium and N.sativa singly and combined reduced the ALT and AST level in serum and also have hepato protection potential.
In conclusion, the extract of Artemisia absinthium and Nigella sativa plant was used for the treatment of liver injury. These plant extracts have flavonoids and phenolic compounds that act as antioxidant properties as well as reduce the AST and ALT level against PARP-induced liver injury. Maybe it is associated with suppressing oxidative stress. The results show that the extract of Artemisia Absinthium and Nigella Sativa has potential against hepatitis and in the future its use as therapeutic medicine against liver injury.
Conclusion
In our study significantly higher level of aminotransferases is due to higher PARP induction in liver injury. A. absinthium and N.sativa singly and combined reduced the ALT and AST level in serum and also have hepato protection potential. We found that the DPPH assay has a strong negative correlation with the HepG2 cell line which indicates that DPPH decreases cell growth through the ROS scavenging mechanism. This study proved that the plant extract is used against APAP hepatic injury and it is also associated with oxidative stress in the body. The extract of Artemisia absinthium and Nigella sativa plant used for the treatment of the liver injury. These plant extracts have flavonoids and phenolic compounds that act as antioxidant properties as well as reduce the AST and ALT level against PARP-induced liver injury. Maybe it is associated with suppressing oxidative stress. The results show that the extract of Artemisia absinthium and Nigella sativa has potential against hepatitis and in the future its use as therapeutic medicine against liver injury.
Funding
This research has no funding’s.
Conflict of InterestAll authors have no conflict of interest
Consent for Publication
This study is based on research.
Acknowledgment
This research study is self-funded.
Availability of Data and Materials
The data associated with a paper is available, the data available on demand through email contact of co-author.
Ethical Approval
All applicable international, national, and institutional guidelines for the care and use.
REFERENCES
- Efferth T, Oesch F. The immunosuppressive activity of artemisini type drugs towards inflammatory and autoimmune diseases. Med Res Rev. 2021;41(6):3023-3061.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma P, Arora A. Clinical presentation of alcoholic liver disease and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease: Spectrum and diagnosis. Trans Gas Hepa. 2020;37:5.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Nakov R, and Velikova T. Chemical metabolism of xenobiotics by gut microbiota. Drug Metabolism. 2020;21(4):260-269.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sayiner M, Golabi P, Younossi ZM. Disease burden of hepatocellular carcinoma: A global perspective. Digest Disc Sci. 2019;64(4):910-7.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Lee J, Han Y, Wang W, et al. Phytochemicals in cancer immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy. Bio Mol. 2021;11(8):1107.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zageer DS, Hantoosh SF. Insight into drugs induce liver toxicity. Drugs Liver Toxi. 2021;57:1-202.
[Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Shareef SH, Ibrahim IA, Alzahrani AR, et al. Hepatoprotective effects of methanolic extract of green tea against thioacetamide-induced liver injury in sprague dawley rats. Saudi J Bio Sci. 2022;29(1):564-573.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Khare P, Kishore K, Sharma DK. Historical aspects, medicinal uses, phytochemistry and pharmacological review of Bauhinia variegate. Asian J Pharm Pharmacol. 2018;4(5):546-562.
- Mazhar MW, Sikandar M, Mahmood J, et al. Molecular analysis of HCV real time pcr in multan Pakistan. J Virology Anti Res. 2021;10(4):53.
- Pandey MM, Rastogi S, Rawat AK. Saussurea costus: Botanical, chemical and pharmacological review of an ayurvedic medicinal plant. J Ethno Pharma. 2007;110(3):379-390.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Choi YK, Cho SG, Woo SM, et al. Saussurea lappa Clarke-derived costunolide prevents TNFα-induced breast cancer cell migration and invasion by inhibiting NF-κB activity. Alter Med. 2013.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kwong S, Meyerson C, Zheng W, et al. Acute hepatitis and acute liver failure: Pathologic diagnosis and differential diagnosis. Diagnostic Pathology 2019;36(6):404-414.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Uchida NS, Silva-Filho SE, Cardia GF, et al. Hepatoprotective effect of citral on acetaminophen-induced liver toxicity in mice. Alter Med. 2017.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sobeh M, Mahmoud MF, Abdelfattah MA, et al. Albizia harveyi: Phytochemical profiling, antioxidant, antidiabetic and hepatoprotective activities of the bark extract. Med Chem Res. 2017;26(12):3091-105.
- Bell LN, Vuppalanchi R, Watkins PB, et al. Serum proteomic profiling in patients with drug‐induced liver injury. Alim Pharma Therap. 2012;35(5):600-12.
[CrossRef] [Google Scholar] [PubMed]